Understanding Melasma
Melasma is a prevalent skin condition that causes dark patches, primarily on the face. It commonly affects individuals over 35 years old and is particularly frequent in Indian skin due to increased melanin production. The excessive accumulation of melanin in specific areas leads to noticeable pigmentation.

Causes of Melasma
- Hormonal Influences:
- Hormonal changes play a significant role for melasma development.
- It Commonly occurs during the perimenopausal stage.
- Melasma is frequently triggered by hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, with a possibility of fading within a year post-pregnancy.
- Sun Exposure:
- UVA rays are a primary contributor to melasma.
- Both UVA and UVB rays stimulate excessive melanin production, intensifying pigmentation.
- Genetic Factors:
- Approximately 30% of cases have a hereditary component.
Effective Treatment Approaches
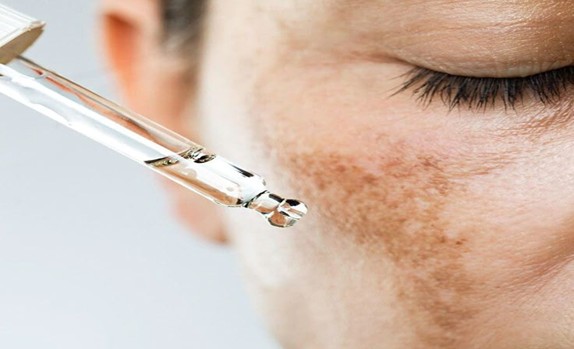
While melasma can be managed effectively, it is not completely curable. Treatment requires consistent, long-term care to prevent recurrence. It’s crucial to commit to an ongoing skincare routine for sustained results.
Topical Solutions
- Cleansers:
- Opt for face washes enriched with Vitamin C, Niacinamide, or Glycolic Acid.
- If using heavy-duty creams, a gentle cleanser is recommended to avoid skin irritation.
- Moisturizers:
- Choose formulations containing Niacinamide, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Hyaluronic Acid, Kojic Acid, and Alpha Arbutin.
- These ingredients work synergistically to enhance skin health and treatment effectiveness.
- Sunscreen:
- A critical step in melasma management.
- Select sunscreens with depigmenting agents, Niacinamide, or Vitamin C along with your spf, pa++ or bluelight protection for additional skin benefits.
- Dermatologist-Prescribed Creams:
- Triple combination creams usually recommended under medical supervision.
- Should be used periodically, with alternative active ingredients introduced when discontinuing usage so its better to consult s dermatologist for a better opinion.
Advanced Treatment Procedures
- After consistent use of topical treatments for 3-4 months, professional procedures may be considered, and maintenance sessions may be required for up to 12 sessions.:
- Chemical Peels – Gently exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation.
- Laser Therapy – Targets excessive melanin, improving skin tone.
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy – Enhances skin repair and helps fade dark patches.
Can Home Remedies Work?
- DIY or kitchen-based remedies are not effective for treating melasma.
- Instead, opt for skincare products containing Niacinamide, Kojic Acid, Vitamin C, and Alpha Arbutin.
- Introduce these ingredients gradually to monitor skin response.
Oral Supplements for Melasma Control
- Glutathione – Aids in skin brightening and overall complexion improvement.
- Vitamin C – Provides antioxidant protection and helps regulate pigmentation.
- Pycnogenol – A natural extract that helps reduce melanin production.
- Tranexamic Acid – A promising treatment for stubborn melasma (should be taken only under medical guidance).
Final Thoughts

- Consult a dermatologist before beginning any over-the-counter treatment.
- Melasma management is a long-term commitment that requires consistency and maintenance.
- Follow expert guidance and skincare protocols to achieve the best results.
With a dedicated and structured approach, melasma can be effectively controlled, leading to a healthier and more radiant complexion.




